Accessing data anywhere, anytime is crucial because it empowers individuals and businesses to make informed decisions on the go. Whether it’s checking emails on a smartphone during a commute or accessing project files from a remote location, this flexibility enhances productivity and efficiency.
Technology has evolved significantly to enable this level of data accessibility. From the advent of cloud computing, which allows storage and retrieval of data over the internet, to the proliferation of mobile devices equipped with high-speed internet connectivity, accessing data has become easier than ever. Additionally, advancements in internet of things (IoT) technology have enabled seamless data access from interconnected devices, further enhancing convenience.
Table of Contents
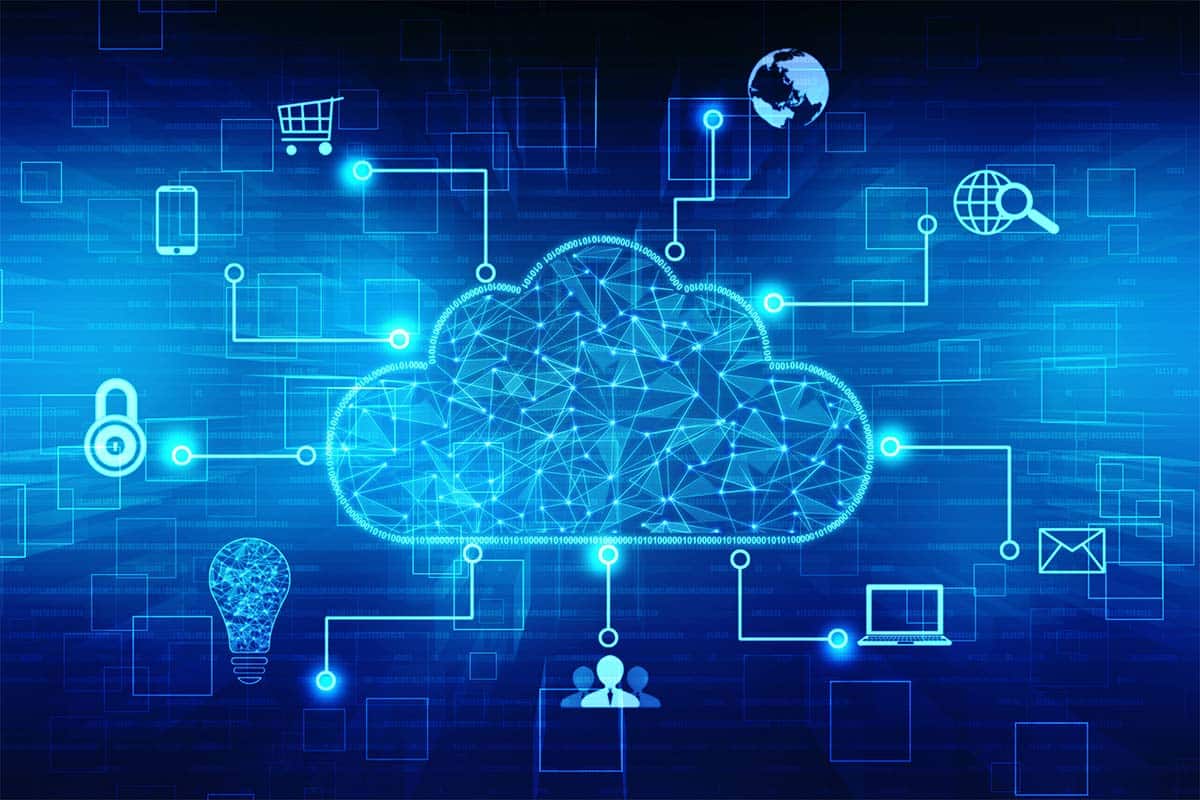
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing means using remote servers on the internet to store, manage, and process data instead of using local servers or personal computers.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
- Scalability: Users can easily scale up or down their computing resources based on their needs. This flexibility ensures they have the right amount of computing power at all times.
- Flexibility: Access computing resources from anywhere with an internet connection. Whether you’re at home, in the office, or traveling, you can reach your data.
- Cost-Efficiency: Pay only for the resources you use, avoiding the need for expensive infrastructure investments. This model is particularly beneficial for small businesses and startups.
Seamless Collaboration
Teams can work together on documents or projects in real-time, regardless of their physical location. This fosters innovation and agility within businesses, improving productivity and efficiency.
Popular Cloud Computing Providers
Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform are some of the leading cloud computing service providers. They offer a wide range of services tailored to different business needs.
Impact of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has become essential for businesses and individuals, empowering them to access powerful computing resources without heavy upfront investment or maintenance. It has revolutionized the way data is stored, managed, and accessed, driving innovation and digital transformation across industries.
Mobile Technology
Mobile technology refers to devices such as smartphones and tablets, as well as the applications and services they enable, that allow users to access data and perform tasks while on the move.
Benefits of Mobile Technology
- Accessibility: Users can access data and applications from anywhere with network coverage, freeing them from the constraints of a fixed location.
- Portability: Mobile devices are lightweight and compact, allowing users to carry them easily and access data on the go.
- Convenience: Mobile technology enables users to perform tasks such as checking emails, managing calendars, and collaborating with others, all from the palm of their hand.
Role in Data Access
Mobile devices play a crucial role in data access, allowing users to retrieve information, communicate with others, and complete tasks regardless of their location. A plethora of mobile applications are available, offering access to various services and data sources, from social media platforms to productivity tools. Mobile data access can be hindered by factors such as network connectivity issues and device compatibility, which need to be addressed for seamless user experience.
Future of Mobile Technology
Mobile technology continues to evolve rapidly, with advancements such as 5G connectivity and augmented reality shaping the future of data access on mobile devices.
As mobile technology becomes more integrated into daily life, its impact on how we access and interact with data is expected to grow, driving further innovation and connectivity.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of interconnected devices, sensors, and objects that collect and exchange data over the internet without human intervention. These devices can range from household appliances and wearable gadgets to industrial machinery and smart city infrastructure.
Impact on Data Accessibility
IoT technology enables seamless access to data from various sources, providing real-time insights into processes, environments, and behaviors. This data accessibility enhances decision-making, efficiency, and convenience across industries and everyday life.
Real-world Applications
IoT is deployed in diverse applications, including smart homes, healthcare monitoring systems, industrial automation, and environmental monitoring. These applications allow users to remotely monitor and control devices, optimize operations, and improve resource management.
Challenges and Concerns
Despite its benefits, IoT presents challenges related to data security, privacy, and interoperability. Safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring compatibility among different IoT devices and platforms are ongoing priorities for IoT adoption and implementation.
Future Trends
The proliferation of IoT devices and advancements in connectivity technologies, such as 5G, are expected to accelerate the growth of IoT ecosystems. Future trends include edge computing, where data processing occurs closer to the source, and AI integration for intelligent data analysis and decision-making.
Remote Access Technologies
Remote access technologies allow users to connect to and interact with a computer or network from a different location. This enables individuals to access data, applications, and resources as if they were physically present at the remote location.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): VPNs create secure, encrypted connections over the internet, allowing users to access private networks securely from anywhere. They ensure data confidentiality and integrity, making them essential for remote work, secure browsing, and accessing restricted resources.
- Remote Desktop: Remote desktop solutions enable users to control a computer remotely from another device. This allows for seamless access to files, applications, and desktop interfaces, facilitating collaboration, troubleshooting, and remote IT support.
- Secure File Transfer Protocols: Secure file transfer protocols, such as SSH (Secure Shell) and SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol), provide encrypted channels for transferring files between devices or servers. They ensure data security during transmission, preventing unauthorized access or interception.
- Challenges and Solutions: Remote access technologies face challenges related to network latency, bandwidth limitations, and security vulnerabilities. Mitigating these challenges requires implementing robust security measures, optimizing network performance, and adhering to best practices for remote access management.
- Future Directions: Advancements in remote access technologies, such as improved encryption algorithms, network optimization techniques, and integration with cloud services, will enhance data connectivity and security for remote users. Additionally, the proliferation of remote work and digital collaboration tools will drive innovation in remote access solutions.
Conclusion
Technology has made it easy for people to get data whenever and wherever they need it. Cloud computing lets us store and access data over the internet without needing physical storage. Mobile devices, like smartphones, allow us to access information even while we’re on the move.
Additionally, the Internet of Things (IoT) connects devices and objects to share data without human involvement. Remote access technologies, such as VPNs and remote desktops, further enhance data accessibility by letting us connect to networks and computers from afar. Looking ahead, advancements like 5G and edge computing promise to make data even more available,